Other Flags
France
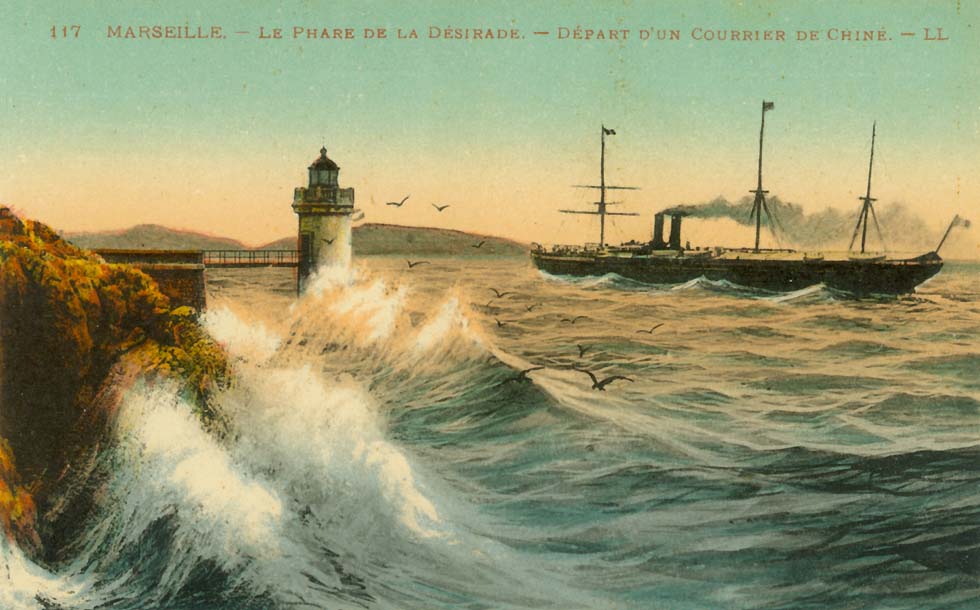

An Indochina mail steamer after departure from Marseilles (old card, coll. WS)
Under Napoleon III, France took possession of Saigon in 1859-61. Mail for that outpost was carried by the P&O as far as Singapore, where the French navy took over. In autumn of 1862 the first mail transport without British support left Marseilles on the steamer "Neva" to Alexandria, proceeding through Egypt by rail and from Suez on board of the "Imperatrice" of the Compagnie des Services Maritimes des Messageries Imperiales. After completion of the Suez Canal, the company inaugurated the first direct service between Marseilles and South East Asia in April 1870, before its name was abbreviated to Compagnie des Messageries Maritimes after Napoleon's abdication in 1871. Fighting in Asia however continued and the colony Indochina was formed not before 1887.
Cook's timetable listed towards the end of the 19th century Messageries Maritimes with monthly departures Marseilles - Yokohama via Djibouti, Colombo, Saigon and Shanghai, and a monthly service via Bombay. The timetables of the 1920's showed the lines Marseilles - Yokohama via Saigon, Marseilles - Haiphong via Tourane and every two months a departure for Sydney and Brisbane. Chargeurs Reunis added services to Haiphong in Indochina, from Bordeaux.
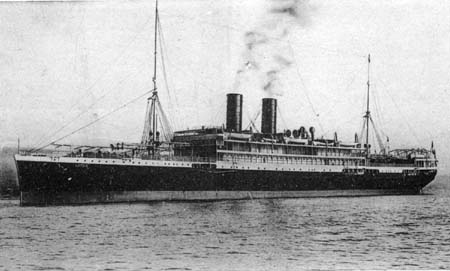
"Lotus", Messageries Maritimes (old card, coll. WS)
|

"Porthos", Messageries Maritimes (old card)
|
Messageries Maritimes introduced in 1922 the "Aramis" (14,825 gt), in 1931 the "Georges Philippar" (16,990 gt), both the first of new series. Returning form her maiden voyage, the "Georges Philippar" sank near the Horn of Africa, caused by fire. In1930 for the first time a motor-ship, the "Eridan" (9,928 gt), was used on the Sydney line, later extended to Nouvelle Caledonie (Noumea). With her two brown square funnels she showed a strange new style.
During World War II Japan invaded Indochina, in 1954 communist Vietcong defeated French troops and until 1975 Vietnam and Cambodia were tortured by wars. The "Eridan", from 1947 used on the route to Madagascar, Reunion and Mauritius, had one or two trips to Haiphong in 1953, probably transporting troops of the French Foreign Legion. Then she crossed the Pacific until 1956. Also the "Pasteur", originally intended for the Cie. Sudatlantique, served as a trooper (in 1959 she became the "Bremen" of NDL). The steamers "Cambodge" (13,217 gt), and her consorts were introduced in the 50s on the Marseilles - Saigon - Yokohama route. After 1969 the "Cambodge" could still be seen for years on the Mediterranean as the cruise ship "Stella Solaris" of Sun Line.
Scannen 10-10-C
"Stella Solaris" of Sun Line, ex "Cambodge" of Messageries Maritimes, Istanbul 1977 (WS)
Austria
When the Suez Canal was under construction, Oesterreichischer Lloyd (Austrian Lloyd) placed orders for the steamers "Apis" and "Sphinx" (1,200 gt) for India services. Around 1870 the line Trieste - Bombay was opened, later followed by services to Calcutta and Hong Kong. In 1871 the company became renamed as Oesterreichisch - Ungarischer Lloyd, but after two decades that addition was dropped, Hungary was no longer willing to finance the Bombay service. In 1886/88 "Imperator" and "Imperatrix" (c. 4,000 gt each) were built for the Hong Kong line, in 1892 Shanghai and one year later Kobe and Yokohama routes were opened. Before World War I a fast line ("Eillinie") Trieste - Bombay with the steamers "Gablonz" and "Marienbad", an Eillinie Trieste - Shanghai with the "Koerber", a mail line Trieste - Kobe / Yokohama and a freight line Trieste - Calcutta taking the Suez Canal went in operation. After World War I, Trieste has been annexed by Italy, granting a freeport to Austria.
Italy

Folder after WWII (coll. WS)
|

"Victoria" of 1932, Lloyd Triestino (official card, coll. WS)
|
In 1869 the Suez Canal was opened and immediately the Italian company Rubattino used it. Rubattino & Co. got a contract in 1872 for the first Italian mail line to India. In 1881 Rubattino and Florio were united and formed the Navigazione Generale Italiana (NGI). Towards the end of the century, Cook's timetable listed NGI services from Genoa to Bombay, Hong Kong and to Massawa. Bradshaw of 1914 showed a monthly Naples - Bombay service run by the Societa Marittima Italiana. After WWI the Lloyd Sabaudo entered the migration business. Lloyd Triestino became the successor of Oesterreichischer Lloyd under participation of the Cosulich family. In the '20s the timetable showed its services to Bombay, Kobe and a route by the Societa Marittima Italiana from Genoa to Bombay. A Genoa - Brisbane Service was provided by the Lloyd Triestino with four modest motor vessels "Esquilino", "Viminale", "Romolo" and "Remo" (8,600 resp. 8,800 gt) then on charter to Lloyd Sabaudo / NGI, which were amalgamated into 'Italia' Flotte Reunite in 1932. A re-organisation transferred these services in 1937 back to Lloyd Triestino. In 1932 the Lloyd Triestino introduced the 13,098-ton motor ship "Victoria", a beauty with two buff funnels, described as a luxury liner Trieste - Alexandria, before outbreak of WWII however listed (e.g. by Weyers) providing Far East services. In 1942 she was sunk by a submarine.
After WWII, Trieste was a "Territorio Libero" under Allied control until 1954. In 1953 Lloyd Triestino introduced the new motor ships "Asia" and "Victoria" (11,695 gt each) on Karachi and Hong Kong services and in 1963 steamer "Galileo Galilei" and S.S. "Guglielmo Marconi" (27,005 gt, 24 knots) on the route Genoa - Naples - Messina - Port Said - Suez - Aden - Fremantle - Melbourne - Sydney. These white ships with one streamlined funnel stood as symbols for elegant Italian design. They were sold and refurbished for cruises in the '70s. The "Victoria", sold in 1974 to Adriatica, became later the YWAM Mercy Ship "Anastasis". The 'Galileo Galilei" cruised for Chandris as "Meridian" and the "Giglielmo Marconi" as "Costa Riviera".
 "Victoria" (II), Lloyd Triestino (official card, coll. WS)
"Victoria" (II), Lloyd Triestino (official card, coll. WS)
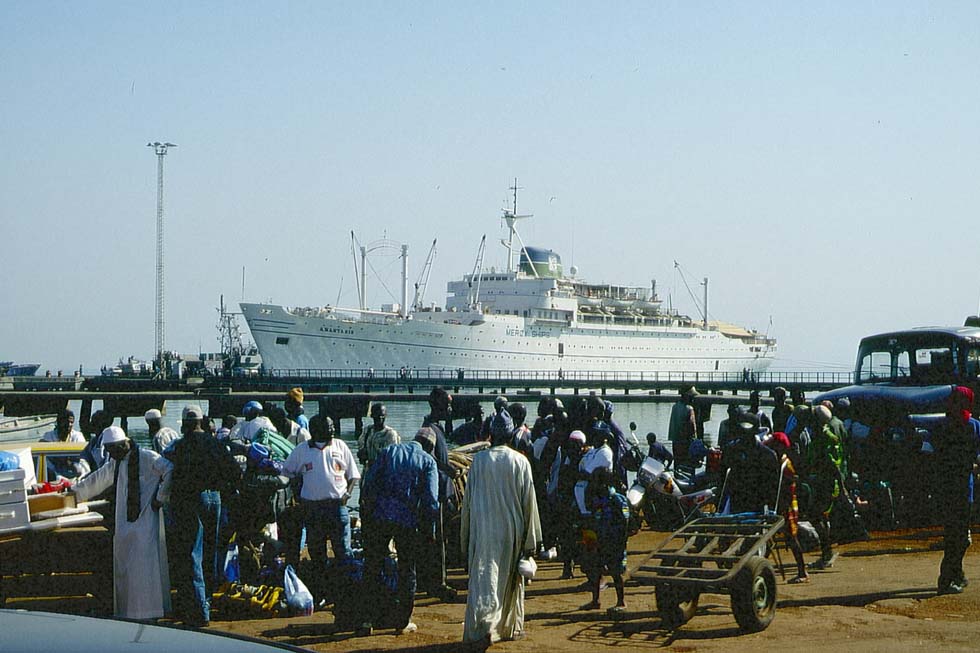

The former "Victoria" (II) of Lloyd Triestino, as "Anastasis" at Banjul, Gambia, 2000 (WS)
The Sitmar Line, founded in 1938 by the Russian immigrant Alexandr Vlasov, started in 1950 emigrant services Bremerhaven - Sydney with the motor vessel "Fairsea" (11,833 gt), the rebuilt U.S. Navy escort carrier "Charger". In 1952 followed the steamer "Castel Felice" (12,149 gt, the former "Kenya" of British India Line) on services first from Genoa, occasionally joined by the "Castel Bianco" (II), built as a US freighter and then by the "Fairsky" (12,664 gt), the former escort carrier "Barnes". In 1964 the steamer "Fairstar" (23,764 gt), completed in 1957 as the Bibby Line troopship "Oxfordshire", took up Australia services under Liberian flag for Fairline, one of the Vlasov group's subsidiaries (all information by J.M. Maber). The history to follow is described with the chapter Cruises/ End of Liners.
The Cogedar Line undertook voyages with their white ships mainly for migrants from Genoa and Bremerhaven. Their motor ship "Aurelia" (10,022 gt) was the once "Huascaran" of Hapag and the "Flavia" (15,465 gt) had been the "Media" of Cunard. Flotta Lauro got known with "Achille Lauro" (23,629 gt), ex "Willem Ruys" of Rotterdamsche Lloyd (temporarily Europe-Canada Line) and "Angelina Lauro" (20,565 gt), ex "Oranje" of S.M. Nederland. After refurbishment in 1965 they had became really beautiful ships and were put on a Bremerhaven - New Zealand route. In 1972, years after the Suez Canal had been closed, regular service gave way to cruises. Around 1950 even the 36 years old "Roma" (ex "Medina" of the Mallory S.S.Co.) undertook some Australia voyages for the C.N. San Miguel.
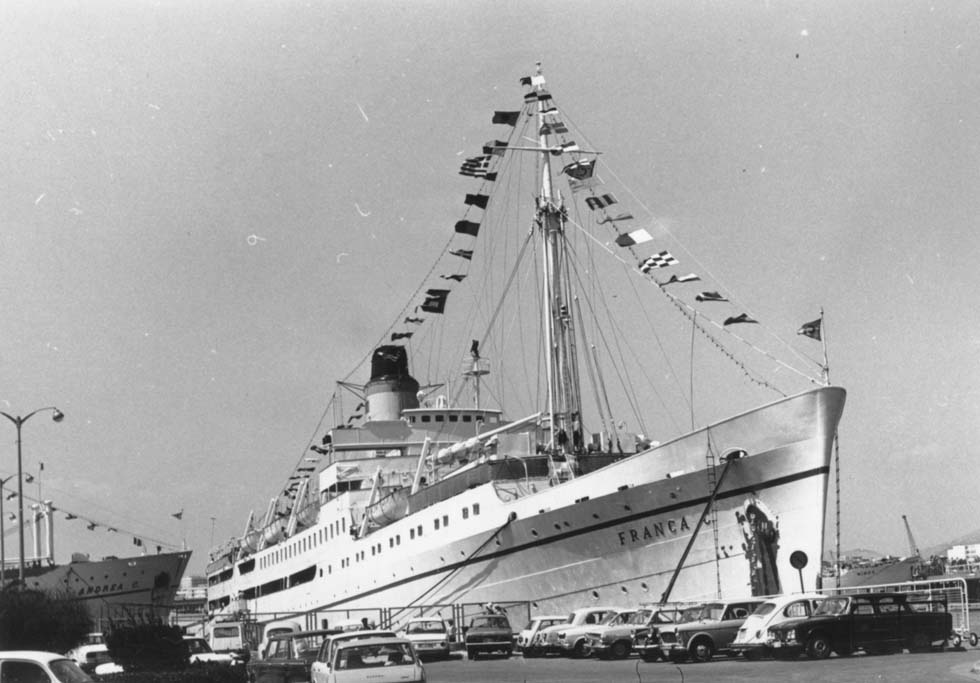

"Franca C", ex "Roma", Piraeus 1973 (WS)
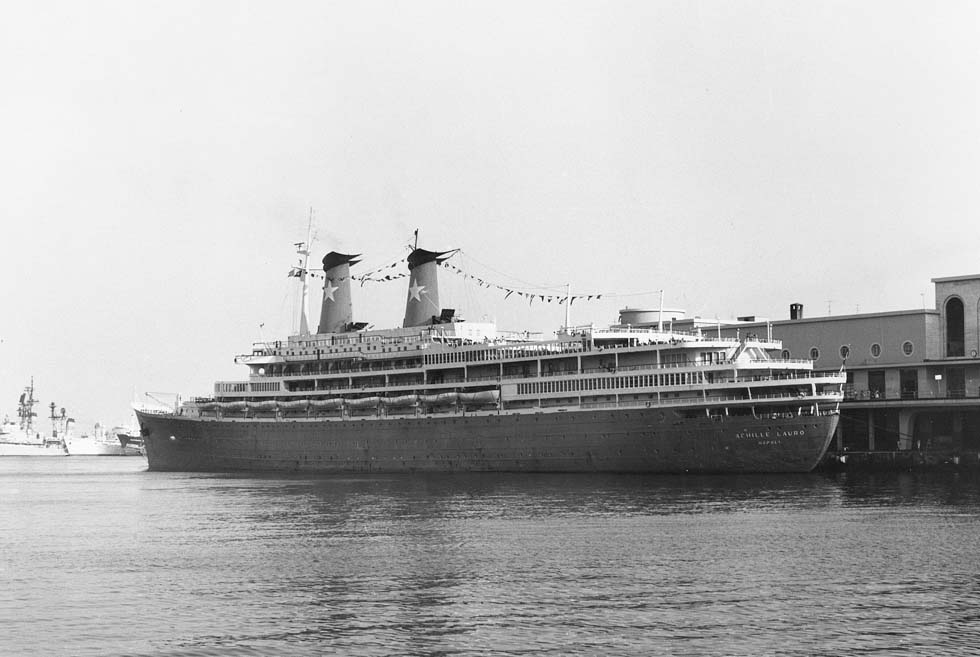

"Achille Lauro", Naples, Ocean terminal 1978 (WS)
Germany
The last European power which acquired colonies in the 1880's has been Germany under Kaiser Wilhelm I. In order to maintain connection to her territories in the remote Pacific area, Deutsch-Neuguinea, Kaiser-Wilhelms-Land, Bismarck-Archipel, Samoa, Salomon and Micronesian Islands, well-working shipping services had to be established. Already before that time, Hendschel's Telegraph timetable of 1856 showed services Hamburg - Melbourne - Sydney via the Cape by R.M.Sloman's Packetschiffahrt, initially with sailing-ships, from 1881 as Sloman-Austral-Linie with steam. In 1881 chancellor Bismarck proposed a subsidized mail steamer line to East Asia. Four years later a contract was granted to the well-known Norddeutscher Lloyd (NDL) for Asia and Australia services. At that time the Kingsin-Linie provided a Far East service and the Australia-Sloman-Linie an Australia service, with small steamers however. In 1886 the "Oder" (3,116 gt) and the "Salier" (3,102 gt) took up the NDL services Bremerhaven- Shanghai and Bremerhaven - Colombo - Adelaide - Melbourne - Sydney. A new Deutsch-Australische Dampfschiffs-Gesellschaft started Sydney services in 1888, but confined them to cargo in 1894. Under leadership of Dr. Heinrich Wiegand the NDL acquired the East Indian Steamship Co., the Scottish Oriental Steamship Co. and the Kingsin-Linie. In 1900 the Hamburg-Amerika Linie (Hapag) entered the Far East business with the steamers "Hamburg" and "Kiautschau", but reduced it to passenger-cargo services in 1904.
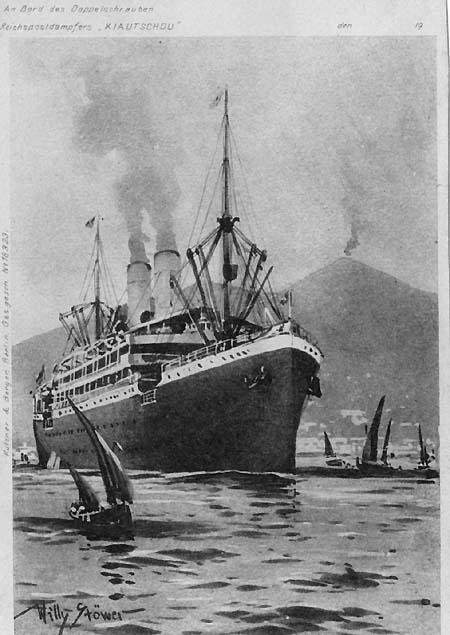 "Kiautschau", Hapag (old card, coll. WS)
"Kiautschau", Hapag (old card, coll. WS)
For the Far East mail and passenger services the NDL put to work from 1886/87 the "Oder" "Neckar", "Nuernberg" and "Braunschweig", then the larger "Preussen" class, the "Muenchen" class, the Prinzen class, from 1903/08 the Feldherrn class series I and from 1906/08 series II (c.9,000 gt), the "Buelow", "Kleist", "Yorck", "Luetzow", "Derfflinger" and "Goeben". For Australian mail services the NDL employed various ships: the "Kaiser Wilhelm II (6,990 gt), "Prinzregent Luitpold" (6,595 gt), "Friedrich der Grosse" and "Barbarossa (10,914 gt), "Grosser Kurfuerst" (13,182 gt), "Bremen" (11,570 gt), and "Koenigin Luise" (10,710 gt), from 1904 the Feldherrn class series I and from 1907/08 series II, "Roon", "Buelow", "Yorck" and "Kleist" (according to Orrie Mueller: 50 Jahre Ostasien - und Australdienst des Norddeutschen Lloyd). In 1908 the Lloyd-Express train Hamburg Altona - Genoa of CIWL in connection with NDL was introduced, continued until 1914 as part of the Riviera-Express, but these were only seasonal de-luxe trains. The mail for the NDL steamers was conveyed to Italian harbours by ordinary trains.
An interlude was the Trieste - Bombay service of Deutsche Ost-Afrika-Linie (DOAL), started in 1904. It was the answer to a new East Africa service of Oestereichischer Lloyd. In 1906 both uneconomic routes were closed down. For East Africa - India services see chapter Branch Lines / Africa.
In consequence of WWI, Germany lost all colonial territories. The NDL could re-introduce freight and then also passenger services to the Far East not before 1922. In the same year the NDL restarted Australia services, in cooperation with the British firm Alfred Holt &Co. In 1924 a joint Far East service became organized, working a regular once-weekly A-line Bremen-Kobe, operated by NDL, Hapag, Alfred Holt & Co., Ellermann & Bucknal SS. Co., and a second-ranking B-line. On the A-line the new steamers of the "Saarbruecken" class (c.9,400 gt), the M.S. "Fulda" and the old "Derfflinger" were employed in the same schedule. Yokohoma was served by the Hugo Stinnes company, while the Rickmers-Linie provided services to Dairen, "if possible" to Vladivostok. In 1926 Hapag swallowed the Deutsch-Austral, Kosmos and their stinnes shares. In 1935 the NDL started fast services to the Far East with the new steamers "Scharnhorst", "Potsdam" and in 1936 the "Gneisenau", which became very popular, being the fastest and most comfortably appointed ships in the entire operation area. "The "Scharnhost" of 18,184 tons, built for a speed of 21 to 23 knots, had a turbo-electric power transmission, instead of the geared turbines of her consorts. The similar "Potsdam" was initially commissioned by Hapag. When WWII started, the "Scharnhorst" stayed in Japan, was sold to the government in 1942, was rebuilt in 1943 into the aircraft carrier "Shinyo" and was sunk by submarine in 1944.
Also in Germany the "Gneisenau" and "Potsdam" should have been rebuilt into aircraft carriers, but after a few preparations the project ended.
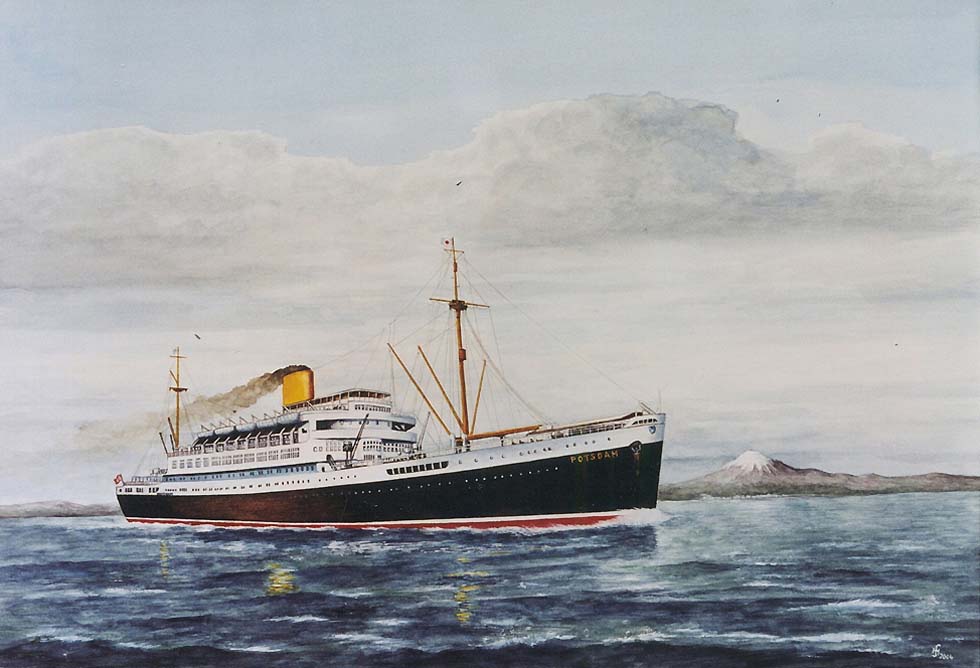

"Potsdam", NDL, at the coast of Japan (painting by Heribert Schroepfer)
World War II had stopped again the German liners. Years after the war NDL and Hapag resumed a joint combined passenger-cargo service by new motor-ships in 1954 with Kobe as terminal, but dropped passenger shipment in the '70s.
Spain and Portugal
The Philippines, a Spanish colony, were connected by a P&O branch line. Much later, in 1837, Marques del Campo acquired the "Vinuelas" for Philippine services. In 1883 she became the "Ignacio de Loyola" of the Compania Trasatlantica, which started a monthly service Barcelona - Manila via the Suez Canal, Colombo and Singapore. Two years later they got the mail contract, held hitherto by the Marques del Campo. After the colony was lost to the USA in 1898, services continued for some time. Bradshaw's timetable of 1914 pointed out a route from Liverpool via Barcelona to Manila. Later on the company's interests have been concentrated on the Atlantic, their initial field of activity. Little is known about Portuguese services to the Far East. Historian Curt Frick mentioned the small motor-ships "Timor" and "India" of the Companhia Colonial de Navigacao on a route Lisbon - Suez - Macao - Dili, East Timor, from 1951.
Japan
 "Fushimi Maru", Nippon Yusen Kaisha (old card, coll. WS)
"Fushimi Maru", Nippon Yusen Kaisha (old card, coll. WS)
The Japanese mail steamship company Nippon Yusen Kaisha, created in 1865 by amalgamation of the Kiodo Ungu Kaisha and the Yubin Kisen Mitsubishi Kaisha, inaugurated services to England and the European continent in 1896, according to historian Laurence Dunn. Cook's timetable of June 1897 listed only Yokohama - Bombay services. The European line was started by the "Tosa Maru" (5,000 gt), followed by bigger ships, such as the "Awa Maru" (6,000 gt) in 1903, the K-class (c. 8,000 gt) in 1908 and the "Suwa Maru" (10,672 gt), "Fushimi Maru" and "Yasaka Maru" in 1914. They were nice steamers, painted black/white with one black funnel. Bradshaw's timetable of 1914 showed fortnightly services from Antwerp, alternating with fortnightly services from London, to Japan.
In December 1915 the "Yasaka Maru" was sunk in the Mediterranean. Nippon Yusen Kaisha changed therefore on the Cape route. In 1922 the "Suwa Maru" and the "Fushimi Maru" re-opened the Suez route together with four new, slightly smaller ships of the H-class. There were fortnightly departures from Hamburg, alternating
with the London services to Yokohama. In November 1939 the "Terukuni Maru", one of a pair of motor ships of 1930, was hit by a mine on the river Thames. Then Nippon Yusen Kaisha dropped the passenger service to Europe for ever.
Russia
Under Tsar Alexander II, Russia occupied the coast of the 'Peter the Great Gulf' and erected in 1860 its naval base Vladivostok. Construction of the Trans Siberian railway began in 1891 and the East-Chinese railway was constituted in 1896, targeting to connect the more suitable harbour Port Arthur on the shore of the Yellow Sea. In 1898 Port Arthur was ceded to Russia by the colonial powers, thus warding off the Japanese aggression on the mainland. The Russo-Japanese War of 1904-1905 was Japan's answer.
Already in 1877 the Tsar founded the Volunteer Fleet or Dobrolyot, serving civilian and military purposes with auxiliary cruisers, described as a 'Patriotic Squadron'. The ships with a black-topped red funnel were built for services between Odessa on the Black Sea, Shanghai and Vladivostok, a route started in 1880. Nagasaki was the ice-free port for winter months. From 1890 a fleet of 7 ships is reported, but about the first vessels used there is no information. In 1900 the fleet had expanded to 15 ships, among others second-hand vessels. The "Kazan" (ex "Adria" of Hapag) went aground off Ceylon in 1905 and was wrecked. A historic postcard shows the "Moskva", described (by collector Dr. R. Plantey) as the former "Angara" of 7,800 tons, built in 1898 for the Russian government, captured by the Japanese in 1904, renamed "Anegama Maru", returned to Russia in 1916. She had been used (according to TheShipsList) by the navy, sank in 1922 and was scrapped in 1950. Weyers Flottentaschenbuch recorded still in the 50s a somewhat similarly-looking naval training-ship, the "Komsomoljetz", built in 1902 as "Okean", obviously never listed for the Volunteer Fleet. Roughly a dozen ships were registered in 1918 for the Shipping Controller of London, some of them listed in 1923 for an 'Anglo-Russian Volunteer Fleet'. Nevertheless Russian ships had their fate in Asian waters: In 1927 the "Pamiat Lenina" of Sovtorgflot (ex "Kishinoff" of the Volunteer Fleet) was seized by a Chinese gunboat and in 1941 the "Simferopol" was bombed by the Japanese at Hong Kong (for more information see the Web site TheShipsList).

"Moskva", ex "Angara", "Anegama Maru" (old card, coll. WS)
|

Vladivostok in the first years of the 20th century (official photo)
|
N.R.P. Bonsor mentioned the Russian Voluntary Fleet and recorded also another, more commercial service: "The Russian East Asiatic Company was founded in 1900 by the East Asiatic Company of Copenhagen to run a steamship service between Russia and the Far East...". Russia's defeat in the Russo-Japanese War in 1905 and opening of Trans-Siberian rail services to Vladivostok via Manchuria around 1906 made those services rather unimportant.
Seven decades later, when other states closed down regular passenger services on the Indian Ocean, communist countries opened them. The Far Eastern Shipping Co. of the Soviet Union introduced in 1973 the "Fyodor Shalyapin" (21,217 gt), ex "Franconia", on the Southampton-Sydney-Auckland route, followed by the "Leonid Sobinov", (21,846 gt), the former "Carmania", both of Cunard. Then regular services gave way to cruises.
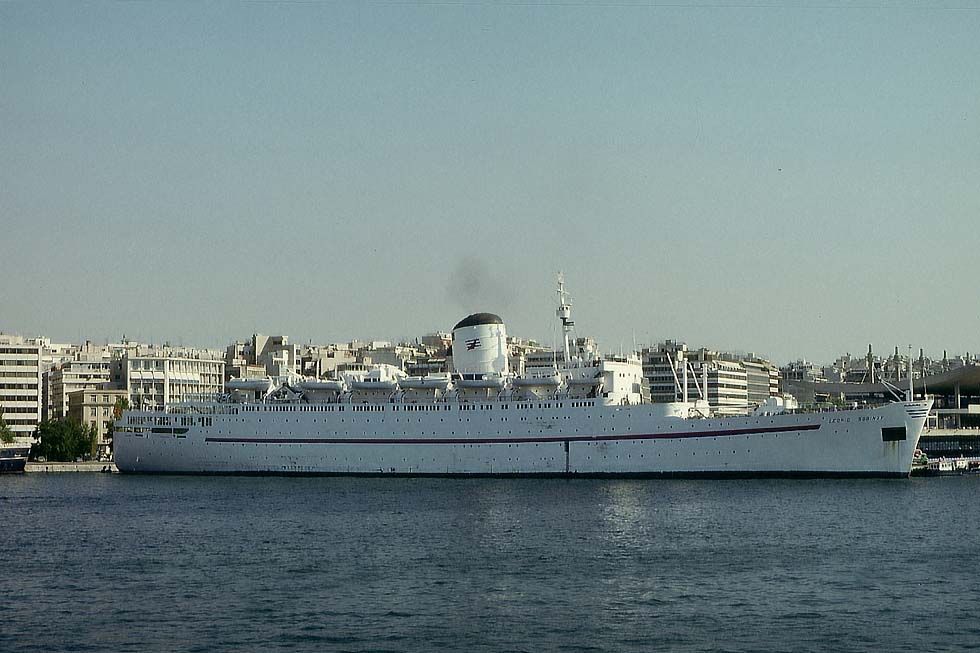

"Leonid Sobinov" ex "Carmania", Piraeus 1990 (WS)
Denmark
Among the shipping lines on the Asia route, the East Asiatic Company of Denmark is specially noteworthy for they were the first to use a diesel-powered ship for crossing the oceans. Already in 1895 Burmeister & Wain dockyards of Copenhagen secured patents for developing that technology, invented by Rudolf Diesel, for ships. H.N. Andersen, the founder of the East Asiatic, ordered in 1910 to build the M.S. "Selandia", a passenger-cargo vessel of 4,964 tons, powered by two 1,250 h.p. diesel engines. In 1912 she had the maiden voyage to Bangkok. Like the similar "Fionia" and "Jutlandia" she was so reliable and economic that the company then ordered exclusively motor ships.
Greece
Before WWII, Greek transoceanic shipping was confined to the North Atlantic. In 1947 however, ELMES opened services Genoa - Piraeus - Fremantle - Melbourne with the "Cyrenia" (7,527 gt), in 1965 joined by the "Tasmania" (11,672 gt, once the British escort aircraft carrier "Archer"). In 1961 these emigrant services ended. In December 1959 a new competitor on the Australia route infuriated the "conference", the cartel of the traditional shipping nations. It was the Greek-Australian Line of Antonis Chandris, starting services with the "Patris" (18,400 gt), the former "Blomfontein Castle" of the Union Castle Line. An original report of a departure of the "Patris" from Piraeus to Australia, showing the passengers, mainly emigrants, with all their waving and all their tears, formed a part of the Greek movie "To the Ship" of Alexis Damianos. After an interlude with the "Britanny" (ex "Bretagne"), Chandris acquired for round-the-world services, initially on the route Southampton - Piraeus - Sydney - Panama - Southampton, three beautiful American ocean liners, in 1963 the "Ellinis" (1932 / 18,565 gt, ex "Lurline" of Matson Line) in 1964 the "Australis" (26,485 gt), once the proud "America" of 1940, and in 1970 the "Britanis" (1932 / 18,655 gt, ex "Monterey", "Matsonia" II, "Lurline" III of Matson Lines). The "Queen Frederica" (1927/21,329 gt, ex "Malolo", "Matsonia" of Matson Lines, "Atlantic"), employed mainly on North Atlantic services, appeared in 1966 on some Sydney voyages. These ships featured the classic lines with two funnels. In 1974 Antonis Chandris and Dimitris Chandris formed Chandris Lines, concentrating more and more on cruises. The white liners with their blue funnels sporting the "X" label bade a majestic farewell.

"Australis" of Chandris, ex "America" (source unknown)
|

"Queen Frederica", laid up at Perama, 1974 (WS)
|
Other Nations
Some rather unknown Australia services were described by J.M.Maber. In 1948 Isak M. Skaugen of Oslo purchased the incomplete ex-German motor ship "Ostmark" and adapted her as "Skaugum" for migrant services Italy - Australia, followed by the former cargo motor vessel "Skaubryn".
 "Skaubryn", I.M. Skaugen (old card, coll. WS)
"Skaubryn", I.M. Skaugen (old card, coll. WS)
In 1949 the Caribbean Land & Shipping Corp. of Switzerland refurbished the M.S. "Nelly" (1940/11,086 gt, built as "Mormacmail" for Moore-McCormack Lines) for migrant traffic Bremen - Melbourne. In 1955 she was transferred to the Europa-Canada Linie as "Seven Seas".
When in 1951 Polish Ocean Lines had been temporarily excluded from calling at New York, they transferred the "Batory" of 1936 to a short-term Gdynia - Bombay service.
Concerning China, Arnold Kludas reported the introduction of the state-owned "Yao Hua" (10,151 gt) on a China - East Africa route in 1967, followed by the "Ming Hua" (14,224 gt, ex "Ancercille") in 1973 and "Yu Hua" (13,694 gt, ex "Nieuw Holland", ex "Randfontein") in 1975. For building the Tanzania-Zambia railway 120,000 Chinese workers had to be brought by ship to Dar es Salaam. From 1981 the "Ming Hua" cruised for some time from Australia for Burns, Philp & Co. and finally she became preserved at Shekou, China.
|